what to do for blood clots in lungs
Overview
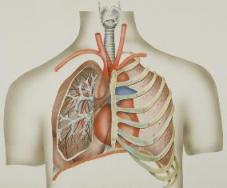
What is a pulmonary embolism?
A pulmonary embolism is a blood jell in the lung that occurs when a clot in another office of the body (ofttimes the leg or arm) moves through the bloodstream and becomes lodged in the claret vessels of the lung. This restricts blood menses to the lungs, lowers oxygen levels in the lungs and increases blood pressure level in the pulmonary arteries.
If a clot develops in a vein and it stays there, information technology's chosen a thrombus. If the clot detaches from the wall of the vein and travels to another part of your trunk, it's called an embolus.
If PEs are not treated quickly, they tin can cause centre or lung harm and even death.
Who is at risk of developing a claret clot?
People at risk for developing a blood clot are those who:
- Have been inactive or immobile for long periods of time due to bed rest or surgery.
- Have a personal or family history of a blood clotting disorder, such equally deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Have a history of cancer or are receiving chemotherapy.
- Sit for prolonged periods.
People at risk for developing a pulmonary embolism include those who:
- Are inactive for long periods of time while traveling via motor vehicle, train or aeroplane.
- Have a history of eye failure or stroke.
- Are overweight or obese.
- Have recently had trauma or injury to a vein, maybe afterward a recent surgery, fracture or due to varicose veins.
- Are meaning or take given birth in the previous half-dozen weeks.
- Are taking birth control pills (oral contraceptives) or hormone replacement therapy.
- Placement of cardinal venous catheters through the arm or leg If you have any of these risk factors and you take had a blood clot, delight talk with your wellness intendance provider then steps tin can be taken to reduce your personal risk.
How serious is a pulmonary embolism?
A pulmonary embolism may dissolve on its own; information technology is seldom fatal when diagnosed and treated properly. Still, if left untreated, it can exist serious, leading to other medical complications, including expiry. A pulmonary embolism tin can:
- Cause heart harm.
- Be life-threatening, depending on the size of the jell.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism vary, depending on the severity of the clot. Although nigh people with a pulmonary embolism feel symptoms, some will not. The outset signs are usually shortness of breath and chest pains that get worse if yous exert yourself. You may cough upwardly bloody sputum. If yous have these symptoms get medical attention right abroad. Pulmonary embolism is serious only very treatable. Quick treatment greatly reduces the risk of decease.
Symptoms may include:
- Sudden shortness of breath -- whether you've been active or at residuum.
- Unexplained sharp pain in your chest, arm, shoulder, neck or jaw. The pain may likewise exist similar to symptoms of a centre assail.
- Cough with or without bloody sputum (mucus).
- Pale, clammy or blueish-colored skin.
- Rapid heartbeat (pulse).
- Excessive sweating.
- In some cases, feeling anxious, calorie-free-headed, faint or passing out.
- Wheezing.
Information technology is besides possible to have a blood clot and not have whatsoever symptoms, so talk over your risk factors with your health care provider.
If you accept whatever symptoms of pulmonary embolism, get medical attention immediately.
What causes pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism may occur:
- When blood collects (or "pools") in a certain office of the trunk (unremarkably an arm or leg). Pooling of claret usually occurs after long periods of inactivity, such as afterward surgery or bed balance.
- When veins take been injured, such equally from a fracture or surgery (especially in the pelvis, hip, knee or leg).
- As a issue of another medical condition, such as cardiovascular disease (including congestive centre failure, atrial fibrillation and center attack) or stroke.
- When clotting factors in the blood are increased, elevated, or in some cases, lowered. Elevated clotting factors tin occur with some types of cancer or in some women taking hormone replacement therapy or nascence control pills. Aberrant or low clotting factors may also occur equally a result of hereditary conditions.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a pulmonary embolism detected?
Pulmonary embolism is commonly detected through the post-obit tests:
- Computed tomography (CT) scan.
- Lung scan.
- Blood tests (including the D-dimer test).
- Pulmonary angiogram.
- Ultrasound of the leg -- helps to identify blood clots in patients who cannot have an X-ray due to dye allergies or who are as well ill to exit their hospital room.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the legs or lungs.
Management and Treatment
How is pulmonary embolism treated?
Handling for pulmonary embolism is typically provided in a hospital, where your condition can be closely monitored.
The length of your treatment and hospital stay will vary, depending on the severity of the clot.
Depending on your medical condition, treatment options may include anticoagulant (claret-thinner) medications, thrombolytic therapy, compression stockings, and sometimes surgery or interventional procedures to amend claret menstruation and reduce the take a chance of futurity claret clots.
Anticoagulant medications
In nigh cases, handling consists of anti- coagulant medications (likewise called blood thinners). Anticoagulants decrease the claret's ability to jell and preclude time to come claret clots.
Anticoagulant medications include warfarin (Coumadin®), heparin, low-molecular weight heparin (such equally Lovenox® or Dalteparin®) and fondaparinux (Arixtra®).
- Warfarin comes in tablet form and is taken orally (by mouth).
- Heparin is a liquid medication and is given either through an intravenous (Four) line that delivers medication directly into the vein, or past subcutaneous (under the skin) injections given in the infirmary.
- Low molecular-weight heparin is injected beneath or under the skin (subcutaneously). Information technology is given in one case or twice a twenty-four hours and tin can exist taken at home.
- Fondaparinux (Arixtra) is a new medication that is injected subcutaneously, one time a 24-hour interval.
Yous and your family volition receive more information about how to take the anticoagulant medication that is prescribed. As with any medication, information technology's important that you sympathise how and when to accept your anticoagulant and to follow your doctor'southward guidelines.
The type of medication you were prescribed, how long yous demand to accept it, and the type of follow-upwardly monitoring you lot'll need depends on your diagnosis. Be sure to continue all scheduled follow-upwards appointments with your doctor and the laboratory so your response to the medication can be monitored closely.
While taking anticoagulants, your follow-up will include frequent blood tests, such as:
- PT-INR: The Prothrombin time (PT or protime)/ International Normalized Ratio (INR) test: Your INR will assistance your wellness care provider determine how fast your blood is clotting and whether your medication dose needs to be changed. This test is used to monitor your status if you are taking Coumadin.
- Activated fractional thromboplastin (aPTT): Measures the fourth dimension it takes blood to clot. This test is used to monitor your condition if you are taking heparin.
- Anti-Xa or Heparin assay: Measures the level of low molecular-weight heparin in the blood. It is usually not necessary to utilize this test unless you are overweight, take kidney affliction or are pregnant.
What are other treatment options?
Compression stockings
Pinch stockings (support hose) aid blood flow in the legs and should be used as prescribed past your doctor. The stockings are normally articulatio genus- high length and compress your legs to prevent the pooling of claret.
Talk with your doctor about how to use your compression stockings, for how long, and how to care for them. It is important to wash compression stockings according to directions to prevent damaging them.
Procedures
If a pulmonary embolism is life-threatening, or if other treatments aren't effective, your dr. may recommend:
- Surgery to remove the embolus from the pulmonary avenue.
- An interventional procedure in which a filter is placed inside the body's largest vein (vena cava filter) then clots tin can be trapped before they enter the lungs.
Thrombolytic therapy
Thrombolytic medications ("clot busters"), including tissue plasminogen activator (TPA), are used to dissolve the clot. Thrombolytics are always given in a infirmary where the patient can be closely monitored. These medications are used in special situations, such every bit if the patient'south blood pressure level is low or if the patient's status is unstable due to the pulmonary embolism.
Prevention
How do I forbid pulmonary embolism?
- Do regularly. If you tin't walk around due to bed remainder, recovery from surgery or extended travel, motion your arms, legs and anxiety for a few minutes each hour. If you lot know you volition demand to sit or correspond long periods, wear compression stockings to encourage blood menstruum.
- Potable enough of fluids, like water and juice, but avoid excess booze and caffeine.
- If you need to be stationary for long periods of fourth dimension, move around for a few minutes each hour: motility your feet and legs, bend your knees, and stand up on tip-toe.
- Practice not smoke.
- Avert crossing your legs.
- Do not wear tight-fitting clothing.
- Lose weight if yous are overweight.
- Elevate your feet for 30 minutes twice a mean solar day.
- Talk to your dr. about reducing your risk factors, peculiarly if you lot or any of your family members accept experienced a blood jell.
Living With
What is follow-upwards care later a pulmonary embolism?
Be sure you discuss and sympathize your follow- up intendance with your doctor. Follow your doc'due south recommendations to reduce the take a chance of another pulmonary embolism.
Proceed all appointments with your physician and the laboratory so your response to prescribed treatments tin can be monitored.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17400-pulmonary-embolism
Belum ada Komentar untuk "what to do for blood clots in lungs"
Posting Komentar